Water Refilling Station Process Flow
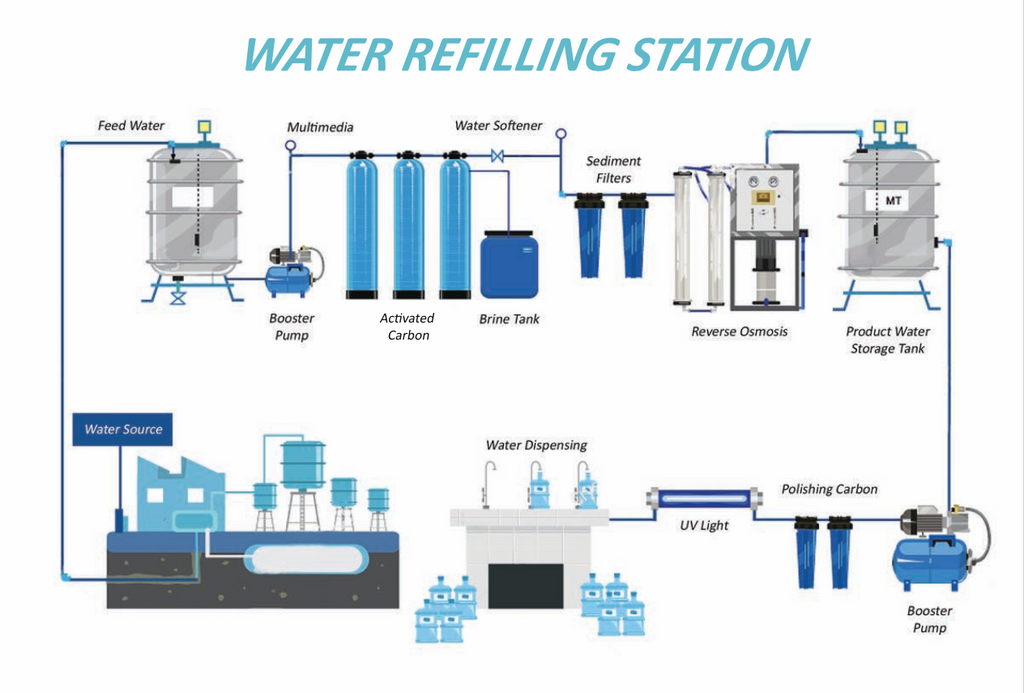
As a water refilling station owner, you must know the basic filtration flow-chart of your system's equipment and its functions. It's as follows:
1) Water Source
There are three types of water sources that can be used for water refiling station:
a) Brackish Water (Deep well) - Usually high in minerals and hardness
b) Surface Water (Spring, River, Shallow Well) - High in turbidity and suspended solids
c) Local Water Utility - this source already passes PNSDW standard and does not require a rigorous water analysis
This is where you store the source water which will be used for purification. This tank is very helpful when the water pressure of your water source is low.
This pump pushes the water thru the filters at a certain pressure and flow rate. This pump is usually balanced with a proper RO pump (more on this later) and properly sized filter tanks.
Raw water is initially treated with silica sand, manganese and anthracite to remove suspended matter down to 10~20μ size and some organics from the water, which if left, will cause a premature drop off in performance from the RO membranes. Our new product AFM® filters down to 4μ at 98% efficiency.
5) Activated Carbon Filter Tank
Raw water is treated with granular activated carbon filtration to remove some organics from the water. The Carbon removes foul taste and odor. It also eliminates yellowish and brownish discoloration brought by inorganic contaminants. The longer the water is in contact with the carbon the more adsorption or catalytic reactions that will take place.
6) Water Softener
This process consists of a Softening and Conditioning Process. It is composed of Resin Beads which attracts mineral contents and converts Hard Water to Soft Water; The Brine Tank (salt compounds) serves as the storage of the industrial salt for the automatic regeneration of the resins.
7) Sediment Filters (Pre-Revserse Osmosis Microfiltration)
A five micron cartridge filter is used as a safeguard to ensure that any fines or particulates are removed from the water, which would otherwise damage the RO membranes.
8) Reverse Osmosis
Pre-treated raw water is then pumped through to the CENTRAL PURIFICATION SYSTEM (RO). RO Technology involves using a high pressure pump to force a portion of the feed water through a semi-permeable membrane. The amount of permeate product water produced varies directly with the feed water pressure and temperature. Since the bulk of the product water contaminants are left on the feed water upstream side of the membrane and would over time, foul or scale the membrane, a portion of the feed water is directed to drain. This stream is called reject water, and the amount of reject water required varies with the amount and type of the contaminants in the water. Each specific feed water source will have a maximum recovery rate or conversion. (i.e. Amount of permeate product water produced divided by the amount of feed water entering the RO unit). The estimated conversion factor determined for this system is 0.35.
9) Product Water Storage Tank
This tank stores the RO water, also known as purified water. The bigger the tank, the more water you store, and the more bottles you can dispense.
10) Product Water Booster Pump
Purified Water is boosted thru multiple faucets with appropriate pressure using booster pump. The stronger the pump, the faster the flow rate of the water at the dispensing area.
11) Polishing Carbon
Polishing here means removing any carryover odor and further enhancement of the taste of the purified water.
12) UV Light
The purified water is passed through a UV sterilizer as a final safeguard against bacteria. Bacterial growth in any high purity water treatment plant will increase the frequency of equipment cleans.
13) Dispensing
This area is where the water is dispensed thru multiple faucets. This area also contains the washing sink for the containers.
Summary
The multi-media and activated carbon filters will remove suspended particulate matter above around 20μ size and chlorine and dissolved organics in the water. Softener will remove any hardness in the water which will avoid premature clogging of the membranes. The micron cartridge filter will remove any fines and particulates. The RO unit will reduce the conductivity of the raw water to 5~10μS/cm and remove most of the bacteria present in the water. The final filtration and UV system will make sure your water will taste good and is bacteria free.
